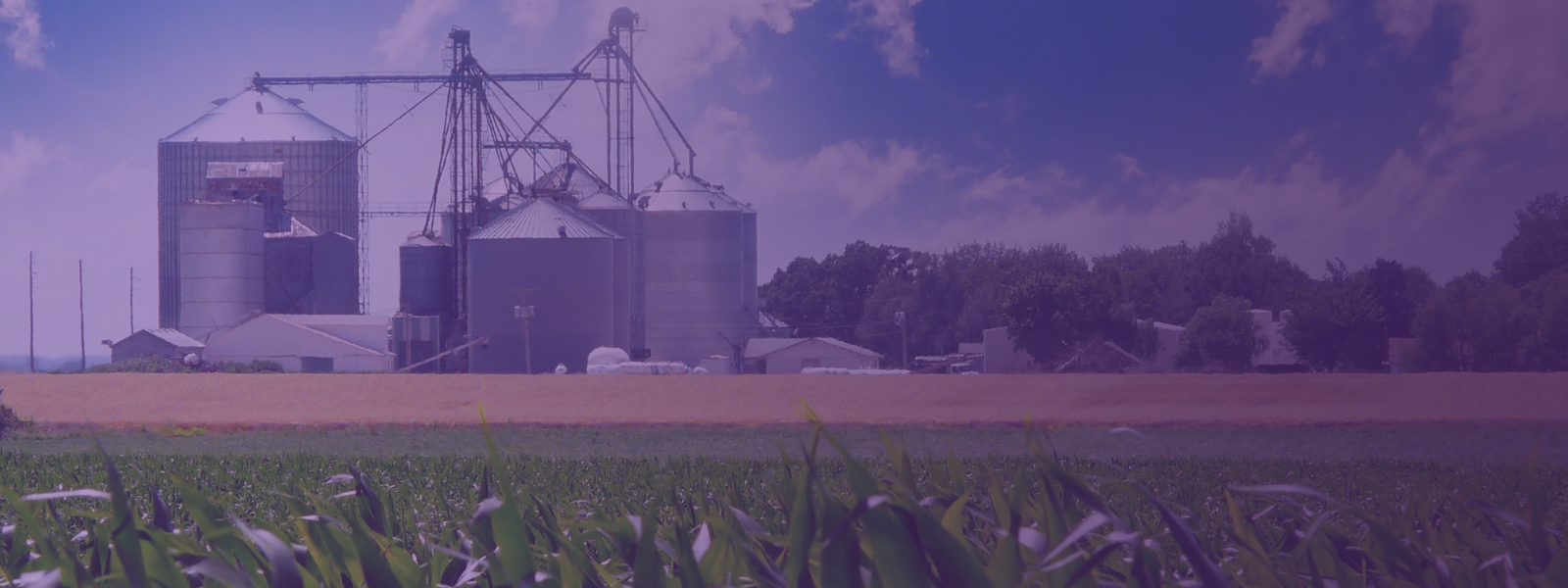
Manufacturers are increasingly developing new ways of using renewable energy to strengthen clean energy competitiveness in various industries. Process heating systems are critical to the global manufacturing industry’s ability to turn raw materials into products.
Renewable energies offer the most effective method for reducing this energy consumption, and manufacturers around the world are exploring unique ways of using renewable energy with this goal in mind.
A summary of the services that Maximpact provides in the application of renewable energy in key industrial processes is shown below.
RENEWABLE ENERGY IN THE CHEMICAL AND PHARMACEUTICAL SECTORS
- Potential for use of heat pumps for low-temperatureprocess heat recovery systems
- The use of waste heat and adsorption chillers to make cold water at 3.4⁰C to displace electric chillers used for process or environmental cooling
- Organic Rankine cycle for converting process waste heat into electricity
- On-sitewind power generation to displace grid power
- The installation of gas engines or a gasturbine to produce electricity and waste heat for process use. Such systems can reduce the energy bills (electric and gas/oil) by as much as 45%
- Solar water heating: Solar air heating systems use the building of conventional steel siding that is painted black to absorb solar radiation. Fresh air entering the bottom of the panels is heated by the sun-heated as it passes over the warm absorber. Small air distribution fans are then used to distribute the hot air around the building interior. Energy savings can result in a payback period of fewer than 3 years
RENEWABLE ENERGY IN THE CEMENT SECTOR
- The potentialfor high-temperatureheat recovery from rotary mills to preheat incoming cold streams or to produce electricity
- The use of waste heat and adsorption chillers to make cold water at 3.4⁰C to displace electric chillers used for process or environmental cooling
- On-sitewind power generation to displace grid power
- The installation of a gasturbine to produce electricity and waste heat for process use. Such systems can reduce the energy bills (electric and gas/oil) in the by as much as 45%
RENEWABLE ENERGY IN THE ALUMINIUM SECTOR
- The potentialfor high-temperatureheat recovery from the smelting process to preheat incoming cold streams or to produce electricity
- The use of waste heat and adsorption chillers to make cold water at 3.4⁰C to displace electric chillers used for process or environmental cooling
- On-sitewind power generation to displace grid power
- The installation of a gasturbine to produce electricity and waste heat for process use. Such systems can reduce the energy bills (electric and gas/oil) in the aluminium sectors by as much as 45%
RENEWABLE ENERGY IN THE PLASTIC SECTOR
- On-sitewind power generation to displace grid power
- Produce a feasibility study for the use of a gas-firedtri-generation system on the site to displace imported grid electricity and also supply chilled water via adsorption chillers to cooling the moulding equipment
RENEWABLE ENERGY IN THE DAIRY SECTOR
- A feasibility study of the installation of solar thermal heating for domestic hot water usage.
- A feasibility study of the installation of Solar PV systems to displace imported grid power.
- A feasibility study for utilising a renewable energy boiler to produce domestic hot water and for process heating using biofuels such as wood pellets or another renewable energy source.
- A feasibility study of installing a gas-firedco-generation or tri-generation systems to supply electricity, heating and cooling in the factory areas requiring cooling,
- Feasibilityto use waste products high in Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) from the dairy processes to produce methane gas in an anaerobic digester unit and supply this methane to run a co-generation or tri-generation systems to displace import grid power and supply hot water, steam and cooling water to the dairy processes.
RENEWABLE ENERGY IN THE MEAT SECTOR
- A feasibility study of the installation of solar water heating for domestic hot water usage.
- A feasibility study of the installation of Solar PV systems to displace imported grid power.
- Feasibility study for utilising a renewable energy boiler to produce hot water for sterilisation of knivesand other deboning equipment using biofuels such as wood pellets or another renewable energy source.
- A feasibility study of installing a co-generation or tri-generation systemsto supply electricity, hot water heating for sterilisation and water at 10⁰C suitable for cooling the meat factory boning hall areas.
- Feasibilityto use waste from the factory to produce methane gas in an anaerobic digester unit and supply this methane to run a co-generation or tri-generation systemsto displace import grid power and supply hot water, steam and cooling water to the factory processes.
RENEWABLE ENERGY IN THE BREWERY SECTOR
- A feasibility study of the installation of solar thermal water heating for domestic hot water usage.
- A feasibility study on the potential for using geothermal energy to provide for domestic hot water and space heating needs.
- A feasibility study of the installation of Solar PV systems to displace imported grid power.
- A feasibility study for utilising a renewable energy boiler to produce domestic hot water and for process heat using biofuels such as wood pellets or another renewable energy source.
- A feasibility study of installing a co-generation or tri-generation systems to supply electricity, heating and high cooling for the fermentation and processing and storage of beer.
- Feasibilityto use waste brewer’s yeast from the fermentation process to produce methane gas in an anaerobic digester unit and supply this methane to run a co-generation or tri-generation systems to displace import grid power and supply hot water, steam and cooling water to the brewing processes.