Natural occurring airflows are used to run wind turbines. Such airflows are generated due to the uneven heating effect the sun has on the earth. Modern utility-scale wind turbines range from around 600 kW to 9 MW of rated power. The power available from the wind is a function of the cube of the wind speed, so as forwind speed increases, power output increases up to the maximum output for the particular turbine. Areas where winds are stronger and more constant, such as offshore and high altitude sites, are preferred locations for wind farms. Typically full load hours of wind turbines vary between 16 and 57 per centannuallybut might be higher in particularly favourable offshore sites.
Wind power by its nature is variable (or intermittent), therefore some form of storage or back-up is inevitably involved. Backup power is normally provided by one of the technologies shown below:
- Connection to an electricity grid system, which may be on a large or small (mini-grid) scale
- Incorporating other electricity producing energy systems (from conventional generating stations through diesel generators to other renewable energy systems)
- Using storage systems such as batteries or, for mechanical systems, storage via water held in a tank. So long as the system is designed to have sufficient storage capacity, whether for energy or product (e.g. water pumped), to cover the periods when the supply is unable to meet the full level of demand, then the outputis always available
Maximpact wind power feasibility studies
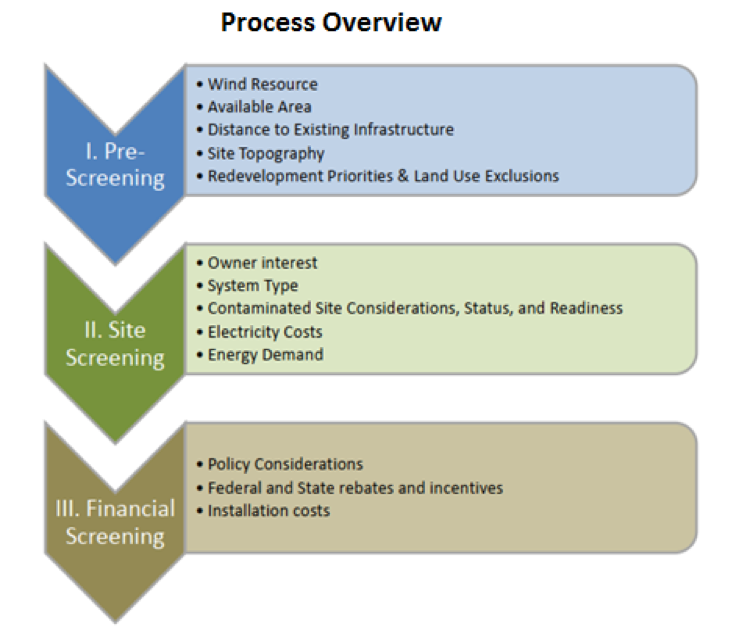
Financial institutions generally require wind study documentation from an independent specialist prior to closing any finance agreement. When determining the potential benefits of renewable energy systems on your site we use mathematical modelling and technology assessment tools in order to assess the technical and economic benefits of deploying wind power systems on your site.
We search for system-level energy solutions that are techno-economically feasible, environmentally desirable, acceptable and realistically implementable in the society. Our perspective is thus different from most of our peers because we go beyond hypothetical techno-economic solutions to the real-world ones to provide you with a sustainable solution.
Maximpact wind energy feasibility study process overview
Other aspects that we can include in our wind energy feasibility study
- Environmental impact assessments
- Power purchase agreement
- Land conveyance agreement
- Ownership structure and agreements
- Construction contract
- Operation and maintenance agreement.
Typical applications of small scale wind power
The list below indicates potential small scale wind power applications (less than 600 kW electrical output)
- Hospitals
- Universities
- Shopping Malls
- Community water supplies and water treatment plants
- Crop irrigation
- Medium size Industrial Sites
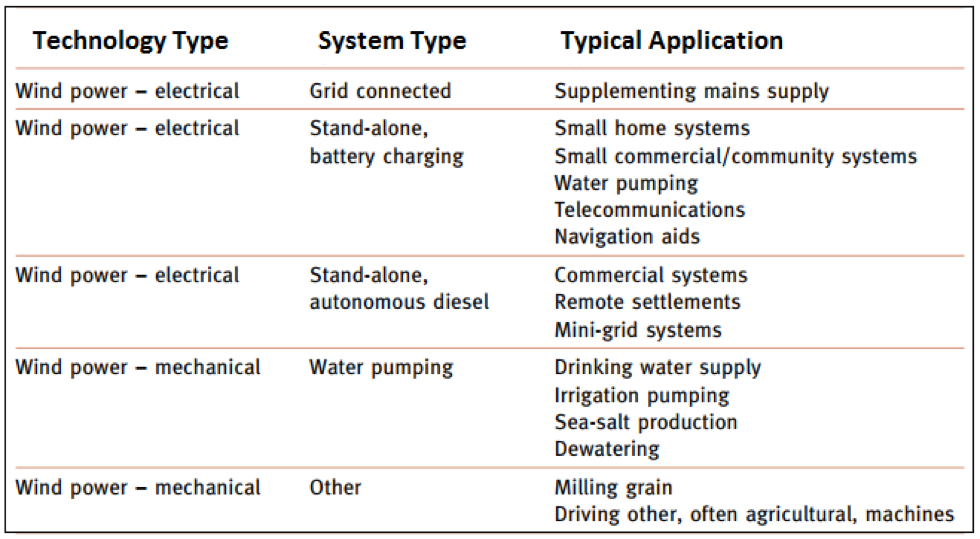
Examples of wind power applications and system type
Wind turbines for water pumping
The most common type of a mechanical wind turbine is the wind pump which uses the wind’s kinetic energy to lift water. Wind-driven pumpsare typically used for water supply (livestock or human settlements), small-scale irrigation or pumping seawater for sea salt production. Here we look at the two main uses which are irrigation and water supply.
There are two distinct categories of wind pumpsbecause the technical, operational and economic requirements are generally different for these two end uses. That is not to say that a water supply wind pump cannot be used for irrigation (they quite often are) but many irrigation designs are generally unsuitable for water supply duties.
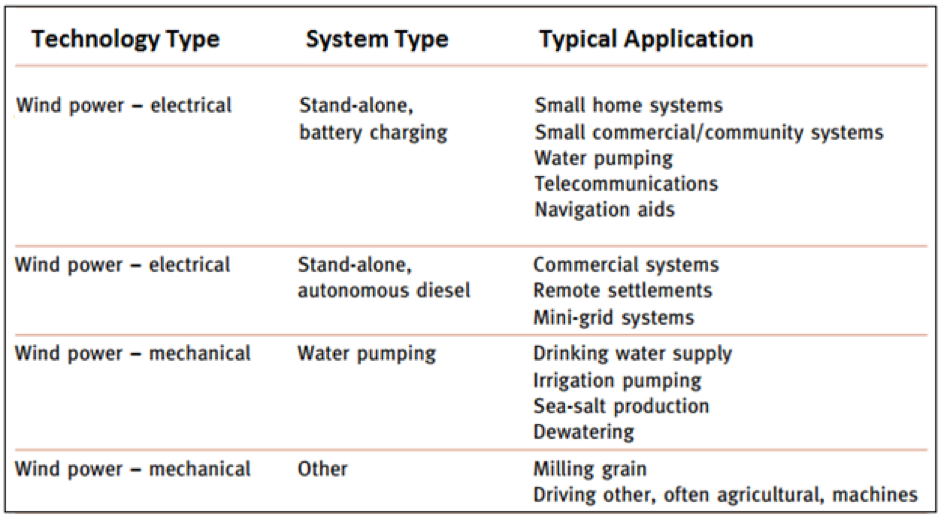
Off-grid applications of wind energy
Wind turbines can also be used to supply energy in off the grid applications as shown in the table below.
Examples of wind power applications and system type
Wind turbines for water pumping
The most common type of a mechanical wind turbine is the wind pump which uses the wind’s kinetic energy to lift water. Wind-driven pumpsare typically used for water supply (livestock or human settlements), small-scale irrigation or pumping seawater for sea salt production. Here we look at the two main uses which are irrigation and water supply.